Trusted ERP Solutions Provider To Small, Medium and Large Enterprises

The Role of ERP in Supply Chain Management for Trading Businesses

I hope you find this blog post insightful. If you’d like our team to handle technology in your business and bring the best ROI, click here.
Efficient supply chain management (SCM) is crucial for the success of trading businesses. At the center of this efficiency lie Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. By integrating inventory management, procurement, and logistics operations, ERP enhances visibility, coordination, and decision-making throughout the supply chain.
How does ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) improve supply chain management?
A supply chain management (SCM) for inventory management is like a big team project where everyone needs to do their part—on time and in sync. In simple terms, Supply Chain Management (SCM) is how businesses move products from idea to customer. It starts with getting raw materials, goes through production and storage, and ends with delivering the product to the buyer.
In trading businesses, this chain doesn’t involve much manufacturing but focuses heavily on sourcing, storing, and selling products quickly and at the right price. Here’s what typically happens:
A customer places an order.
The company checks inventory and finds where the product is stored.
The warehouse ships it to the customer.
Behind the scenes, the company tracks costs, updates inventory, and manages payments.
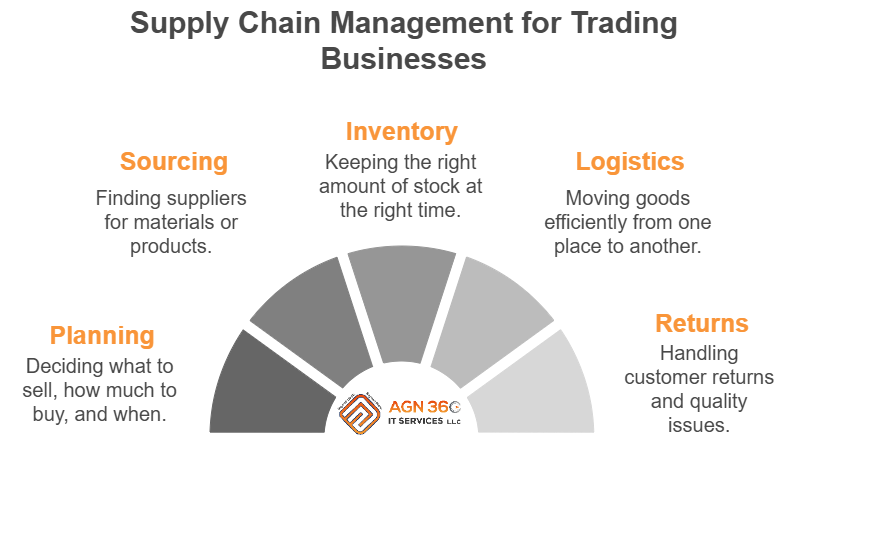
Key parts of SCM:
Planning: Deciding what to sell, how much to buy, and when.
Sourcing: Finding suppliers for materials or products.
Inventory Management: Keeping the right amount of stock at the right time.
Logistics: Moving goods efficiently from one place to another.
Returns: Handling customer returns and quality issues.
SCM might sound complex, but with the right tools—like ERP—it becomes much simpler, even for small businesses.
What Is Enterprise Resource Planning in the Supply Chain Management (SCM)?
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning, but you can consider it your business’s main control center. It connects all the important processes like sales, inventory, procurement, and finance in one digital system. When you hear supply chain management ERP software (SCM), it means ERP designed especially to handle the full flow of goods and services.
In trading businesses, Enterprise Resource Planning doesn’t just help with accounting or HR—it’s deeply connected to how products move. It links every point in your supply chain (SCM) and makes sure everyone, from the purchasing manager to the delivery team, has the info they need when they need it.
How ERP Improves SCM:
Real-time Data: Know what’s in stock, what’s selling, and what’s coming.
Automation: Auto-generate purchase orders, invoices, and delivery notes.
Forecasting: Use past sales to guess future demand.
Integration: Connect departments like finance, warehousing, and sales.
Without ERP, teams often use separate tools and spreadsheets, which leads to mistakes and delays. ERP makes everything smooth, fast, and accurate.

How does ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) improve supply chain management?
A supply chain management (SCM) for inventory management is like a big team project where everyone needs to do their part—on time and in sync. In simple terms, Supply Chain Management (SCM) is how businesses move products from idea to customer. It starts with getting raw materials, goes through production and storage, and ends with delivering the product to the buyer.
In trading businesses, this chain doesn’t involve much manufacturing but focuses heavily on sourcing, storing, and selling products quickly and at the right price. Here’s what typically happens:
A customer places an order.
The company checks inventory and finds where the product is stored.
The warehouse ships it to the customer.
Behind the scenes, the company tracks costs, updates inventory, and manages payments.
Key parts of SCM:
Planning: Deciding what to sell, how much to buy, and when.
Sourcing: Finding suppliers for materials or products.
Inventory Management: Keeping the right amount of stock at the right time.
Logistics: Moving goods efficiently from one place to another.
Returns: Handling customer returns and quality issues.
SCM might sound complex, but with the right tools—like ERP—it becomes much simpler, even for small businesses.
What Is Enterprise Resource Planning in the Supply Chain Management (SCM)?
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning, but you can consider it your business’s main control center. It connects all the important processes like sales, inventory, procurement, and finance in one digital system. When you hear supply chain management ERP software (SCM), it means ERP designed especially to handle the full flow of goods and services.
In trading businesses, Enterprise Resource Planning doesn’t just help with accounting or HR—it’s deeply connected to how products move. It links every point in your supply chain (SCM) and makes sure everyone, from the purchasing manager to the delivery team, has the info they need when they need it.
How ERP Improves SCM:
Real-time Data: Know what’s in stock, what’s selling, and what’s coming.
Automation: Auto-generate purchase orders, invoices, and delivery notes.
Forecasting: Use past sales to guess future demand.
Integration: Connect departments like finance, warehousing, and sales.
Without ERP, teams often use separate tools and spreadsheets, which leads to mistakes and delays. ERP makes everything smooth, fast, and accurate.
The Real Role of ERP in Supply Chain Management (SCM)
In trading businesses, where products move fast and margins are tight, ERP becomes essential. It brings visibility and control.
Here’s how ERP supports every link in the supply chain:
Visibility: See everything from order fulfillment to delivery in one dashboard.
Efficiency: Automate tasks that used to take hours.
Accuracy: Fewer mistakes in stock counts, orders, and payments.
Speed: Ship faster with better coordination between teams.
Scalability: Grow your business without losing track of operations.
ERP systems keep everyone on the same page, from warehouse workers scanning barcodes to managers making financial decisions. This connected view is a game-changer.
Why ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) Matters for Trading Businesses:
Most trading companies rely on moving products quickly and reliably.
Margins can be slim, so errors are costly.
Customers expect fast service ERP helps meet those expectations.
Planning & Demand Forecasting
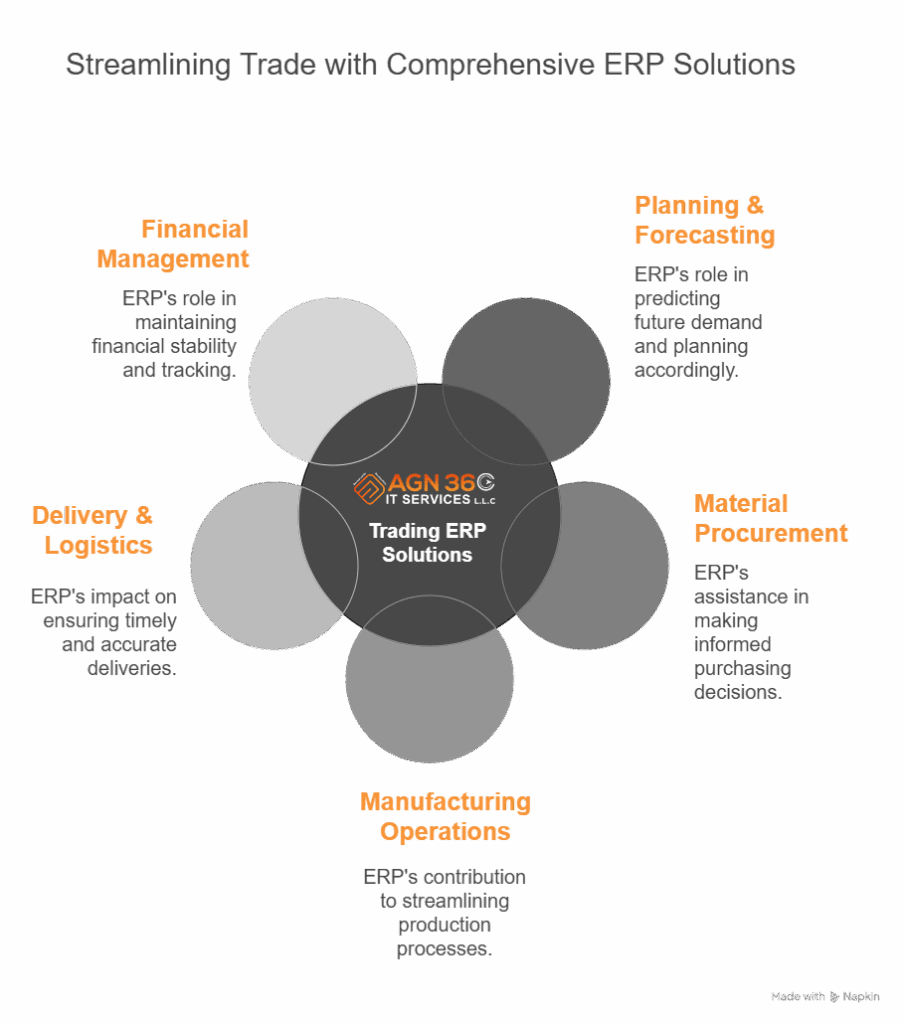
Planning is everything in business. If you guess wrong, you might overstock and lose money—or run out of stock and miss sales. That’s where ERP’s planning tools shine.
With ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), companies can forecast demand using real data. The software looks at past sales, market trends, and even seasons to help you plan better.
ERP helps you plan by:
Analyzing Trends: Which products sell the most in which months?
Setting Targets: How much stock should you have each week or month?
Scheduling Resources: Which team members or machines are needed when?
Without good planning, businesses fly blind. But with ERP, it’s like having a roadmap for the future.
Obtaining Materials
Buying the right products at the right price is a big part of the trading business. ERP systems simplify purchasing by automating requests and comparing supplier options.
What ERP does for purchasing:
Supplier Tracking: Keep a list of trusted vendors and their prices.
Order Automation: Auto-generate purchase orders when stock is low.
Approval Workflows: Send orders to managers for quick sign-off.
This not only saves time but also helps get the best deals and avoid costly delays. With ERP, you don’t have to chase suppliers for updates the system does it for you.
Manufacturing
Even in trading businesses, some goods may be slightly modified or repackaged before selling. This is where manufacturing processes come into play. ERP software in supply chain management (SCM) helps organize this step, even if the business doesn’t do full-scale production.
ERP helps manufacturing by
Scheduling jobs ensures tasks are completed on time and in the right order.
Resource Planning: Matches raw materials with production needs.
Monitoring Progress: Tracks each stage of the process to avoid delays.
ERP systems also flag problems early, like a missing item or equipment delay, so the team can fix it before it affects deliveries. This keeps your operations lean and stress-free.
Delivery
Getting the product to the customer might seem like a final, simple step, but it’s a big deal. Fast, accurate delivery creates happy customers, and unhappy ones usually don’t come back. With ERP, businesses can manage shipments with precision.
How ERP helps with delivery:
Order Fulfillment: Matches orders with the right products and shipping info.
Shipping Labels and Invoices: Automatically generates documents for delivery.
Tracking: Lets customers and staff see where each order is in real time.
Imagine if every order reached the customer on time, without confusion or double-checks. That’s what ERP does: it turns delivery into a well-oiled machine.
Finances
In any business, money is key. Without clear financials, even a successful supply chain can fail. Supply chain management ERP software (SCM) includes financial tools that track every penny moving in and out.
ERP financial tools include:
Cost Tracking: Know how much each product costs to buy, store, and ship.
Profit Margin: See how much money you’re actually making per sale.
Budgeting: Set limits for spending and watch how actual costs compare.
These tools don’t just help accountants; they give business owners the power to make smart, money-saving decisions in real time.
Procurement
Procurement is more than just buying stuff; it’s choosing the best suppliers, negotiating deals, and timing your purchases just right. ERP makes all this easier by organizing data and automating tasks.
With ERP, procurement becomes
Data-Driven: Know exactly which supplier gives the best deal.
Fast: Auto-create purchase orders when stock levels drop.
Controlled: Track every step from supplier selection to payment.
For trading businesses, where profit often depends on tight margins, better buying equals bigger savings, and ERP makes it happen.
Inventory Management
Inventory management can be a nightmare if not managed well. Too much stock means wasted money; too little means lost sales. ERP gives full visibility of your inventory in real time, across multiple warehouses or stores.
ERP improves inventory management by
Real-Time Updates: See stock levels instantly as sales and deliveries happen.
Reorder Points: Set alerts when it’s time to restock.
Location Tracking: Know exactly where every item is stored.
This means no more guesswork, no more running out of bestsellers, and no more over-ordering slow movers.
Production Planning and Scheduling
Even in trading businesses, especially those that assemble, label, or customize products, planning and scheduling are essential. This isn’t about large-scale manufacturing, it’s about making sure every task happens at the right time with the right materials.
ERP takes care of production planning by
Setting Clear Timelines: So every job is completed on time.
Avoiding Delays: By checking material availability before starting.
Balancing Workloads: So no one team or machine is overbooked.
Imagine trying to run a kitchen without knowing which meals need to be made and when. That’s what unplanned production feels like. ERP is like the head chef organizing the entire kitchen.
Order Fulfillment
Managing customer orders is where your business shows its true colors. Customers expect fast service, accurate delivery, and smooth communication. ERP helps make that happen, especially when handling lots of orders.
Here’s how ERP simplifies order management:
Automated Processing: Orders go from online store to warehouse without delays.
Error-Free Info: Correct shipping, billing, and product data, every time.
Customer Updates: Send alerts for order confirmation, dispatch, and delivery.
With supply chain management ERP software, no order falls through the cracks, and customers stay in the loop from the moment they click “Buy” to when the box arrives at their door.
Returns and Quality Control
Sometimes things go wrong—a customer might receive the wrong product or a damaged item. Good businesses fix issues quickly, and ERP helps make that easy. It tracks returns and quality issues so companies can fix problems and learn from them.
ERP features for returns and QC:
Return Authorization: Easy-to-manage return processes with tracking.
Quality Reporting: Tracks patterns in product issues.
Corrective Actions: Helps avoid repeated mistakes.
Case Study: ERP Success in a Real Trading Business
Let’s say a mid-sized trading company called “FastGoods Traders” used to struggle with delays, missing stock, and unhappy customers. Their departments used separate systems, and no one had the full picture.
They adopted supply chain management ERP software (SCM) to connect purchasing, inventory, sales, and delivery. Within six months:
Order processing time dropped by 40%
Inventory errors reduced by 70%
Customer satisfaction improved significantly
Now, FastGoods knows what’s in stock, when to reorder, and how to deliver faster than competitors—all thanks to ERP.
Benefits of Using ERP in Supply Chain Management
Using supply chain management ERP software (SCM) comes with tons of benefits that directly help trading businesses stay competitive and efficient. Here’s how it makes a difference:
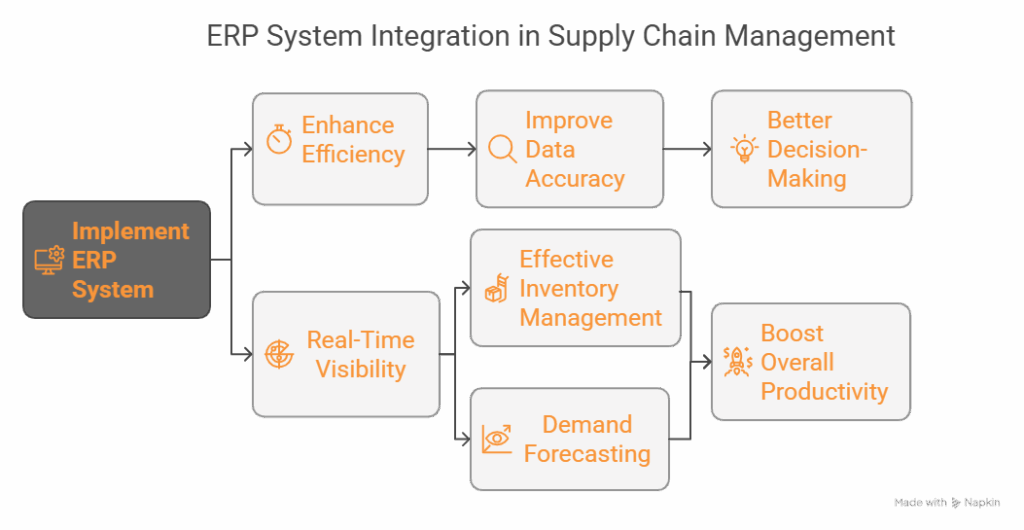
1. Real-Time Visibility
You can instantly see what’s happening with your stock, orders, and deliveries. No more calling warehouses or checking outdated spreadsheets.
2. Better Customer Service
Faster order processing and reliable deliveries mean happier customers. ERP also helps track issues like returns or refunds smoothly.
3. Improved Accuracy
Everything is automated and synced, reducing mistakes in billing, stock levels, and shipping.
4. Cost Savings
ERP reduces waste, prevents over-ordering, and automates tasks that would take hours. All of this adds up to saving money.
5. Faster Decision-Making
With clear reports and dashboards, managers can make quick, smart decisions based on real data, not guesses.
6. Scalability
As your trading business grows, ERP grows with you. You won’t need to switch tools when you scale—just add new features or users.
Challenges of ERP in the Supply Chain
While ERP brings a lot of good things, it’s not without challenges. Here’s what to watch out for:
1. High Initial Costs
ERP software can be pricey at the start, especially for small businesses. But think of it as an investment—it pays off over time.
2. Time-Consuming Implementation
Setting up ERP takes time. You’ll need to train your team, clean up old data, and customize the system for your needs.
3. Change Management
People resist change. Getting everyone used to the new system might be tough at first. Training and support are key.
4. Technical Issues
If you’re not using a cloud-based ERP, you might need IT support. System bugs or network issues can also cause downtime.
5. Integration with Other Tools
Sometimes ERP doesn’t play nicely with your existing tools. You may need extra plugins or developer help to make everything work together.
Key Features to Look for in an ERP System with Supply Chain Management (SCM) Functionality
Choosing the right ERP system is crucial. Here are the must-have features if you’re using ERP to manage your supply chain (SCM):
1. Inventory Tracking
The system should let you view real-time stock levels, set reorder points, and manage multiple warehouses.
2. Order Management
It should automate the full order cycle—from order entry to shipment and invoicing.
3. Procurement Automation
Look for features that handle supplier management, purchase orders, and approvals seamlessly.
4. Demand Forecasting Tools
Good ERP software uses sales history and trends to help you plan inventory smartly.
5. Integration Capabilities
It should easily connect with your e-commerce platforms, CRM, accounting tools, and shipping carriers.
6. Real-Time Reporting
Dashboards and detailed reports help you make data-driven decisions instantly.
7. Returns Management
A built-in process for managing customer returns and tracking quality control issues is essential.
Best ERP systems for supply chain management
SAP Business One
Ideal for small to mid-sized trading companies, SAP Business One offers real-time inventory tracking, multi-warehouse management, and seamless order processing. It’s known for its reliability and deep functionality across procurement and inventory management.
Zoho ERP (Zoho Inventory + Zoho Books + Zoho CRM)
A cost-effective and cloud-based ERP suite ideal for small to mid-sized trading businesses. Zoho offers real-time inventory tracking, warehouse management, order fulfillment, and integrations with e-commerce and shipping platforms like Shopify, Amazon, and FedEx.
Oracle NetSuite
A cloud-based solution designed for mid- to large enterprises, NetSuite provides global inventory visibility, advanced warehouse automation, and integrated fulfillment management. It’s a powerful choice for businesses with complex supply chain needs.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central
Great for SMBs already using Microsoft tools, this ERP features inventory valuation methods, real-time supply chain tracking, and built-in logistics planning. It offers seamless integration with Office 365 and Power BI for extended capabilities.
Odoo ERP
Known for its flexibility and open-source model, Odoo lets businesses pick and customize modules as needed. Its inventory management module includes features like batch transfers, automated reordering, and integration with shipping providers.
Epicor ERP
Tailored for wholesale and distribution companies, Epicor offers strong tools for inventory forecasting, shipping, and multi-location stock control. It supports complex logistics and supply chain scenarios, especially for larger operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
ERP means Enterprise Resource Planning. It’s software that helps businesses manage daily tasks like inventory, sales, purchasing, and more.
Yes! ERP is especially helpful for small businesses that want to grow. It saves time, reduces mistakes, and improves service.
Modern ERP systems are user-friendly and come with training. Most are cloud-based, so you don’t need big servers or IT teams.
ERP does more than track stock. It links inventory with orders, purchases, finance, and shipping in one system.
Some ERPs are expensive, but many affordable options exist. The money saved in mistakes and delays often pays for the system.
An ERP system streamlines Supply Chain Management by integrating all core processes like procurement, production, inventory, order management, and logistics. Key benefits include:
Realtime data visibility across departments
Improved inventory control and reduced stockouts
Faster procurement cycles and supplier collaboration
Enhanced forecasting and demand planning
Better compliance and documentation for global supply chains
To optimize the supply chain, setting up an ERP system involves:
Mapping existing SCM processes and identifying gaps
Selecting ERP modules relevant to supply chain (Inventory, Procurement, WMS, etc.)
Customizing workflows and integration with logistics partners
Configuring realtime dashboards and alerts for supply chain KPIs
Training teams and aligning them with ERP workflows
A dedicated Supply Chain ERP usually includes the following core modules:
Inventory Management
Procurement and Sourcing
Warehouse Management System (WMS)
Order Management
Production and Manufacturing Planning
Logistics and Transportation
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
Demand Forecasting & Analytics
Yes, several ERP vendors offer specialized solutions for SCM. These include:
SAP SCM – For large enterprises with complex global supply chains
Oracle SCM Cloud – Offers flexibility and cloudbased deployment
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management – For midsize to large businesses
Odoo ERP – Modular and affordable for SMEs with customizable supply chain apps
Infor SCM – AIdriven and analyticsbased ERP tailored for supply chains
The cost of implementing a supply chain ERP varies based on business size, complexity, and customization.
When selecting an ERP for supply chain optimization, consider:
Scalability and flexibility of the system
Industryspecific features and best practices
Integration capability with existing tools (e.g., CRM, shipping platforms)
Userfriendly interface and mobile accessibility
Vendor support and ERP partner ecosystem
Strong analytics and reporting tools for decisionmaking
Total cost of ownership (TCO) and ROI potential
It’s the process of sourcing and acquiring goods or services needed for business operations.
It ensures the right materials are purchased at the right time and cost for smooth production.
Key steps include identifying needs, selecting suppliers, purchasing, and managing contracts.
Logistics involves the transportation, warehousing, and delivery of goods.
It ensures timely delivery and reduces costs by optimizing transportation and storage.
The main types are inbound (supplier to company) and outbound (company to customer) logistics.
It’s the ERP function that manages storage, tracking, and movement of inventory.
It improves inventory accuracy, reduces errors, and speeds up order processing
Features include inventory tracking, space optimization, picking/packing, and barcode scanning
It’s the complete process from receiving an order to delivering it to the customer
It directly impacts customer satisfaction and repeat business.
Stages include order processing, inventory picking, packing, shipping, and delivery.

Saeeda Riaz
Partner at AGN IT Services LLC | Strategic IT Partner of 10+ Enterprises
Saeeda Riaz is a seasoned IT consultant with over 23 years of experience in delivering innovative technology solutions to businesses across various industries. As the driving force behind a leading IT solutions company, she specializes in digital transformation, business automation, and software development. Her strategic vision and hands-on expertise help organizations streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and stay ahead in the digital landscape.
Connect on LinkedInContact us for IT Solutions
